Français
Sign up to create an account on the Water Rangers data platform.
Already registered? Link to Micro Water Rangers group to enter your data.
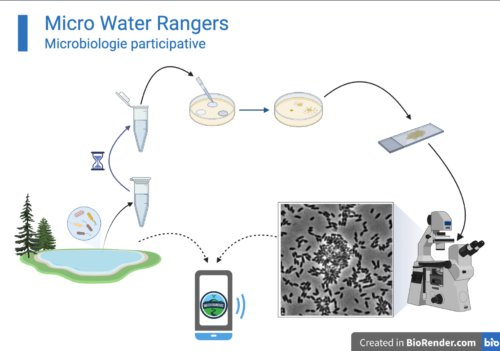
Sample bacteria in the water
A small water sample can contain millions of bacteria! Help us learn more about the bacteria in the water by participating in this citizen science project and conducting microbiology research.
Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotics are chemicals that are toxic to bacteria. Antibiotic medications are used to fight bacterial infections in humans and other animals like livestock and pets. Antibiotics make modern medical procedures, surgeries and treatment of deadly diseases possible.
Many antibiotics were first discovered in bacteria, which produce antibiotics to fight off competing bacteria. Many bacteria have evolved the ability to survive, or resist, the toxic effects of some antibiotics.
We are still learning about which bacteria produce antibiotics and which are resistant. This study seeks to learn where there might be antibiotic resistant bacteria in the waters of our environment.
How to sample with your Micro Water Rangers kit
Visit the Water Rangers website for the protocol to test the water with the kit.
Login and upload your data to the Water Rangers data platform.

- IMPORTANT! Make sure your hands are clean. You want to sample the microbes in the water, not from your skin!
- Record location details on the baggie label.
- Submerge tube in water, snap open lid, and allow tube to fill with water to the 4mL.
- Seal the tube by snapping shut.
- Place in labeled baggie.
- Store sample at room temperature (avoid extreme cold or heat from direct sun).
- Test again! Choose another location or another time to collect a second sample to compare with your first.
Please return tube(s) and kit to Les Scientifines or pick-up location.
Les Scientifines, 525 Dominion St, Montreal, Quebec H3J 2B4
Next steps
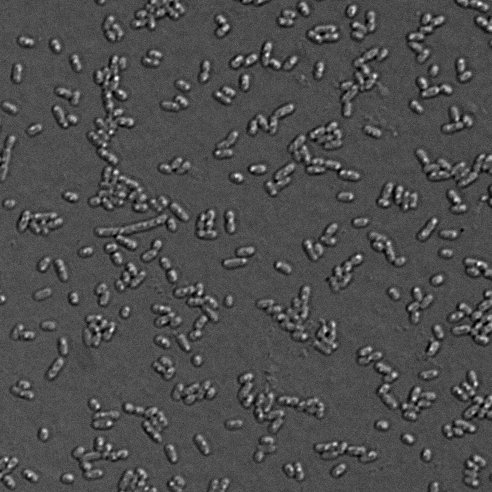
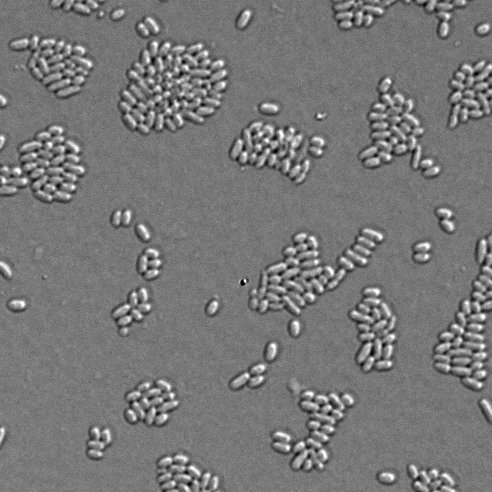
Many of the bacteria in your sample can survive for a very long time in the low-nutrient, low-oxygen conditions of a sample tube. The surviving bacteria can then be grown in the lab in special culture media. Because some microbes can impact human health, these bacterial cultures must be maintained in a laboratory using biosafety precautions. In the lab, the bacteria will be imaged using high-power microscopes.
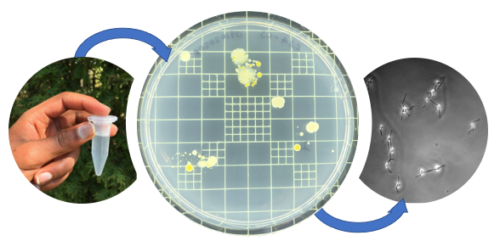
- In the lab, we will grow the bacteria with and without different kinds of antibiotics to analyze which are resistant.
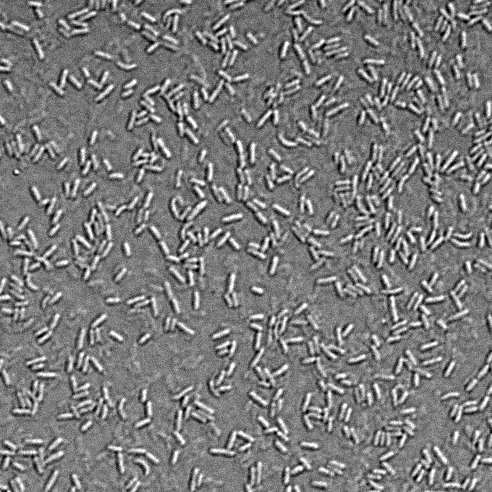
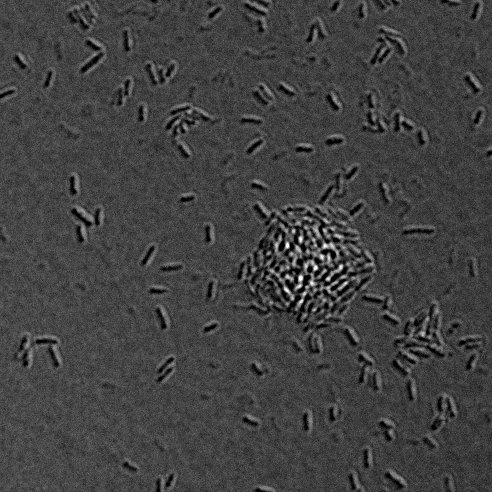
- In the lab, we will use a high-resolution microscope to photograph bacteria in the samples.
- These data will be uploaded to the Water Rangers app so you can view the results and images from the sample(s).
- Check back on the app to visualize the results.
- Generate questions about what you observe, and contact the lab to continue your research!
Thank you for participating in this citizen science study!

Bacteria cultured from water from the Lachine Canal, Montreal, summer 2020, sampled by Les Scientifines.
 Micro Water Rangers guide as PDF
Micro Water Rangers guide as PDF
Thanks to the support from :